Yueyang Outlook
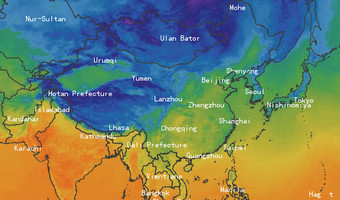
Yueyang City has a subtropical monsoon climate transitioning from central subtropical to northern subtropical. It has the characteristics of four distinct seasons, abundant heat, variable temperature in spring, concentrated rain, drought in summer and autumn, and short severe cold period. The climate in this area is relatively complicated, and there are certain differences between hills and lakes. The average temperature of the coldest month is 4-5℃, and the average temperature of the hottest month is 28-29℃. The annual average temperature is 16.6-17.2℃. The extreme lowest temperature was -18.1℃ (January 30, 1969, Linxiang), and the extreme lowest temperature in the urban area was -11.8℃ (January 23, 1956). The extreme maximum temperature was 40.3°C (July 26, 1971, Pingjiang), and the extreme maximum temperature in the urban area was 39.3°C (July 21, 1971). The frost-free period is about 260-280 days, and the growth period is longer, which is conducive to the growth of various crops. The sunshine is abundant, with 1717~1814 hours of sunshine per year. In a year, the sunshine hours are more in July and August, which is beneficial to the growth of major crops. However, the "three colds" (cold in spring, low temperature in May, cold dew in September) often bring serious harm to agricultural production. The annual precipitation is 1,200 to 1,500 mm, with more mountainous areas than lakes, and more in the south than in the north; more spring and summer, less autumn and winter; from April to June, due to the influence of the summer monsoon, the intensity of rainfall is high, which can easily cause floods; from July to September, Controlled by the Pacific subtropical high pressure zone, it is hot and less rainy, and there are many summer droughts.
 Waning crescent
Waning crescent